Untangling the details, Rezence clarifies How Does A Dns Work 2024: The Definitive Manual
1 What is DNS? A Complete Guide to How DNS Works
- Author: shopify.com
- Published Date: 07/18/2022
- Review: 4.95 (961 vote)
- Summary: · A DNS server works through a process called DNS resolution. A client issues a DNS query for what is known as an “A record” to map a domain name
- Matching search results: Browsing the internet wouldn’t be possible without the domain name system (DNS). The universal nature of the DNS makes it possible for browsers to comb the incalculable well of documentation online and serve the correct page to users in a period of …
- Source: 🔗
Details
2 What is a Domain Name System (DNS) & How Does it Work?
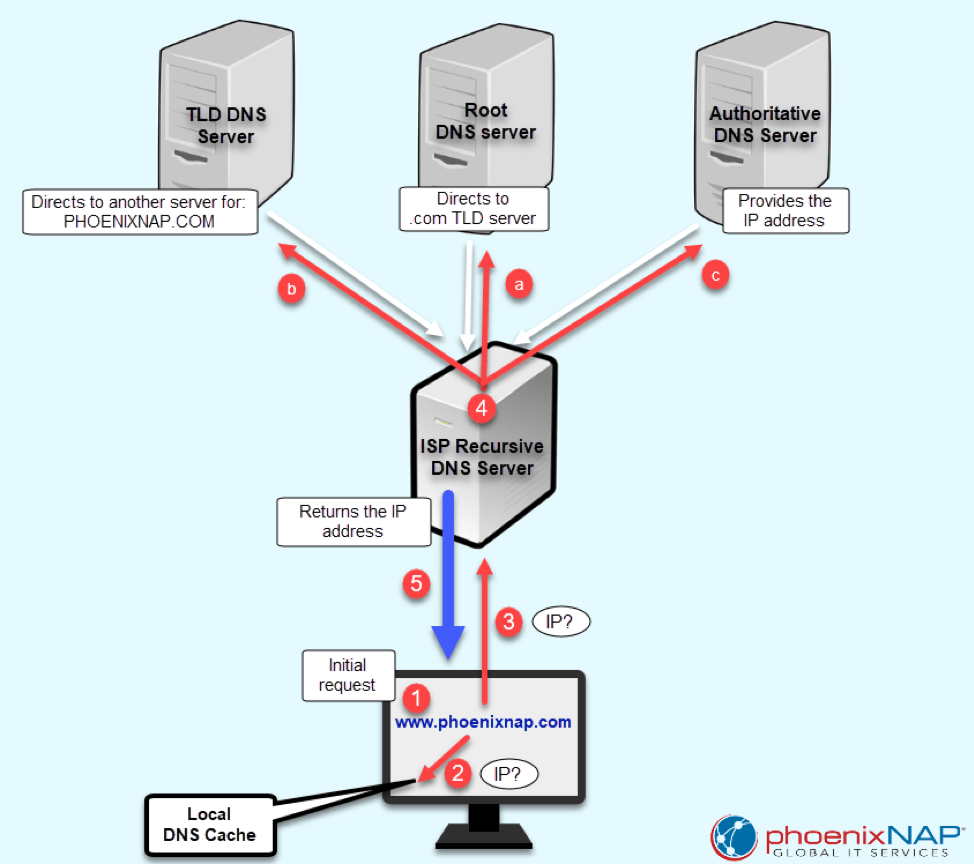
- Author: phoenixnap.com
- Published Date: 07/10/2022
- Review: 4.77 (590 vote)
- Summary: · DNS keeps the record of all domain names and the associated IP addresses. When you type in a URL in your browser, DNS resolves the domain name
- Matching search results: When the DNS cache has the IP data for the website that you are trying to connect to, the page loads immediately. DNS cache expedites this lookup process since the computer contains the information it needs and does not have to forward the request …
- Source: 🔗
Details
3 What Is DNS and How Does It Work?
- Author: knowledgehut.com
- Published Date: 11/20/2021
- Review: 4.5 (213 vote)
- Summary: · The basic function of a DNS is to convert the user-friendly domain name into a corresponding computer-friendly IP address
- Matching search results: Earlier DNS server outage had a significant impact on the business but today due to server monitoring TLD nameservers, root DNS servers and backup recursive, it has become more efficient in resolving the issues. Though most of the outage and failure …
- Source: 🔗
Details
4 What is DNS and how does it work?
- Author: networkworld.com
- Published Date: 10/25/2021
- Review: 4.19 (440 vote)
- Summary: · DNS is organized in a hierarchy. An initial DNS query for an IP address is made to a recursive resolver. This search first leads to a root
- Matching search results: There are currently more than 342 million registered domains, so keeping all those names in a single directory would be cumbersome. Like the internet itself, the directory is distributed around the world on domain name servers that communicate with …
- Source: 🔗
Details
5 What is DNS and how does it work
- Author: linuxhint.com
- Published Date: 09/13/2022
- Review: 4.14 (294 vote)
- Summary: DNS (Domain Name System and NOT Domain Name Server) is the system through which domain names are translated into IP addresses. We can think about the Domain
- Matching search results: DNS (Domain Name System and NOT Domain Name Server) is the system through which domain names are translated into IP addresses. We can think about the Domain Name System as a translator from friendly www.domain.com to IPv4 addresses X.X.X.X (or IPv6 …
- Source: 🔗
Details
6 What is DNS, How it Works Vulnerabilities
- Author: varonis.com
- Published Date: 09/08/2022
- Review: 3.89 (228 vote)
- Summary: · How DNS Works … DNS is such an integral part of the internet that it’s important to understand how it works. Think of DNS like a phone book, but
- Matching search results: DNS (Domain Name System and NOT Domain Name Server) is the system through which domain names are translated into IP addresses. We can think about the Domain Name System as a translator from friendly www.domain.com to IPv4 addresses X.X.X.X (or IPv6 …
- Source: 🔗
7 What Is DNS? Definition & How DNS Servers Work | Fortinet
- Author: fortinet.com
- Published Date: 11/28/2021
- Review: 3.61 (424 vote)
- Summary: A Domain Name System (DNS) turns domain names into IP addresses, which allow browsers to get to websites and other internet resources. Every device on the
- Matching search results: DNS (Domain Name System and NOT Domain Name Server) is the system through which domain names are translated into IP addresses. We can think about the Domain Name System as a translator from friendly www.domain.com to IPv4 addresses X.X.X.X (or IPv6 …
- Source: 🔗
8 How DNS Works – the Domain Name System (Part One)
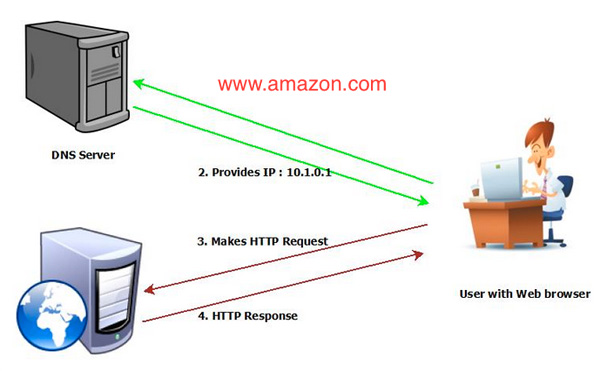
- Author: cloudacademy.com
- Published Date: 07/04/2022
- Review: 3.53 (545 vote)
- Summary: · How DNS Works … When a user types a human-readable address into the browser, the operating system’s DNS client will check for information in a
- Matching search results: While we’ll get to AWS’s Route53 Domain Name System (DNS) service in the second part of this series, I thought it would be helpful to first make sure that we properly understand just how DNS works in general. Once we’re comfortable with the DNS …
- Source: 🔗
Details
9 How Does DNS Work? – Kevin Sookocheff
- Author: sookocheff.com
- Published Date: 07/08/2022
- Review: 3.29 (285 vote)
- Summary: · Remember that domain names are just indexes into the DNS database. For leaf nodes, the data at the node represents an individual host on the
- Matching search results: The data indexed by a domain name is called a resource record. There are several types of records for different types of data. For example, there are unique resource records for mail routing and for or host address information. Each record type …
- Source: 🔗
Details
10 How does DNS Work? – ITGeared
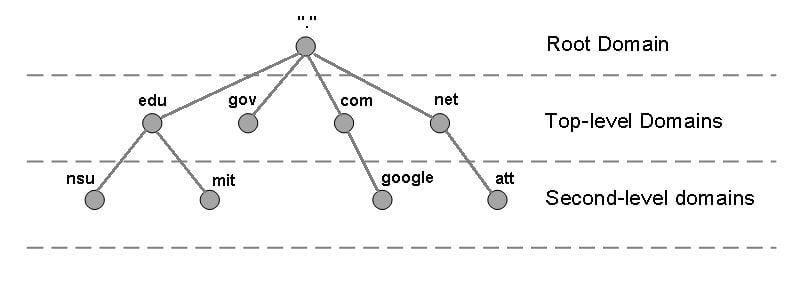
- Author: itgeared.com
- Published Date: 03/16/2022
- Review: 3.01 (576 vote)
- Summary: How does DNS Work? … DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is used for name resolution on a TCP/IP network. Before you can understand what DNS is and where it
- Matching search results: For example, if a server has multiple names associated with a server, you could create a host (A) record called server1 and map that to the IP address of the computer. Then create several alias (CNAME) records, such as www, ftp, mail, that map back …
- Source: 🔗
Details
11 How the Domain Name System (DNS) Works
- Author: verisign.com
- Published Date: 12/31/2021
- Review: 2.99 (151 vote)
- Summary: The Domain Name System (DNS) is an important part of the internet, providing a way to map names (a website you’re seeking) to numbers (the address for the
- Matching search results: For example, if a server has multiple names associated with a server, you could create a host (A) record called server1 and map that to the IP address of the computer. Then create several alias (CNAME) records, such as www, ftp, mail, that map back …
- Source: 🔗
12 What is DNS? | How DNS Works – DNS Made Easy
- Author: dnsmadeeasy.com
- Published Date: 03/08/2022
- Review: 2.84 (96 vote)
- Summary: Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the internet – where computers and services connected to the Internet that resolves domain names to IP
- Matching search results: For example, if a server has multiple names associated with a server, you could create a host (A) record called server1 and map that to the IP address of the computer. Then create several alias (CNAME) records, such as www, ftp, mail, that map back …
- Source: 🔗
13 What is Domain Name System (DNS)?
- Author: infoblox.com
- Published Date: 09/16/2022
- Review: 2.77 (162 vote)
- Summary: The domain name system works much like a phone book where users can search for a requested person and retrieve their phone number. DNS servers translate
- Matching search results: The purpose of DNS is to translate a domain name into the appropriate IP address. This is done by looking up the dns records of the requested domain. There are typically eight steps in this DNS lookup process that follow the information path from …
- Source: 🔗
Details
14 How DNS works
- Author: howdns.works
- Published Date: 04/29/2022
- Review: 2.64 (106 vote)
- Summary: A comic that explains what happens when you browse on the internet
- Matching search results: The purpose of DNS is to translate a domain name into the appropriate IP address. This is done by looking up the dns records of the requested domain. There are typically eight steps in this DNS lookup process that follow the information path from …
- Source: 🔗
15 What is DNS? How Domain Name System works – TechTarget
- Author: techtarget.com
- Published Date: 07/13/2022
- Review: 2.56 (82 vote)
- Summary: How DNS works … DNS servers convert URLs and domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand and use. They translate what a user types into a
- Matching search results: The purpose of DNS is to translate a domain name into the appropriate IP address. This is done by looking up the dns records of the requested domain. There are typically eight steps in this DNS lookup process that follow the information path from …
- Source: 🔗
16 How Domain Name Servers Work
- Author: computer.howstuffworks.com
- Published Date: 03/04/2022
- Review: 2.46 (153 vote)
- Summary: Whether you’re accessing a website or sending e-mail, your computer uses a DNS server to look up the domain name you’re trying
- Matching search results: Computers and other network devices on the internet use an IP address to route your request to the site you’re trying to reach. This is similar to dialing a phone number to connect to the person you’re trying to call. Thanks to DNS, though, you …
- Source: 🔗
Details
17 What Is DNS? Everything You Need to Know About the Web&039s Phone Book
- Author: pcmag.com
- Published Date: 02/11/2022
- Review: 2.36 (125 vote)
- Summary: · Simply put, Domain Name System (DNS) is the phone book of the internet. It’s the system that converts website domain names (hostnames) into
- Matching search results: Once the proper IP address is found, the information is sent back to your browser and the web page loads. The recursive DNS server also stores that IP in its cache memory for a few seconds to a week(Opens in a new window). This is done so that the …
- Source: 🔗
Details
18 Understanding the DNS Process | Liquid Web
- Author: liquidweb.com
- Published Date: 07/17/2022
- Review: 2.1 (97 vote)
- Summary: · How Does the DNS Process Work? · Step 1: Requesting Website Information · Step 2: Contact the Recursive DNS Servers · Step 3: Query the
- Matching search results: Once the proper IP address is found, the information is sent back to your browser and the web page loads. The recursive DNS server also stores that IP in its cache memory for a few seconds to a week(Opens in a new window). This is done so that the …
- Source: 🔗
19 Working of Domain Name System (DNS) Server
- Author: geeksforgeeks.org
- Published Date: 07/22/2022
- Review: 2.1 (150 vote)
- Summary: · DNS resolves names to numbers, to be more specific it resolves domain names to IP addresses. So if you type in a web address in your web browser
- Matching search results: So back to our example, when you type google.com on your web browser DNS server will search through its cache to find a matching IP address for that domain name, and when it finds it it will resolve that domain name to IP address of Google web site, …
- Source: 🔗
Details

